운영체제 & 병렬처리/Multithread
MemoryPool
3DMP
2022. 10. 10. 13:57
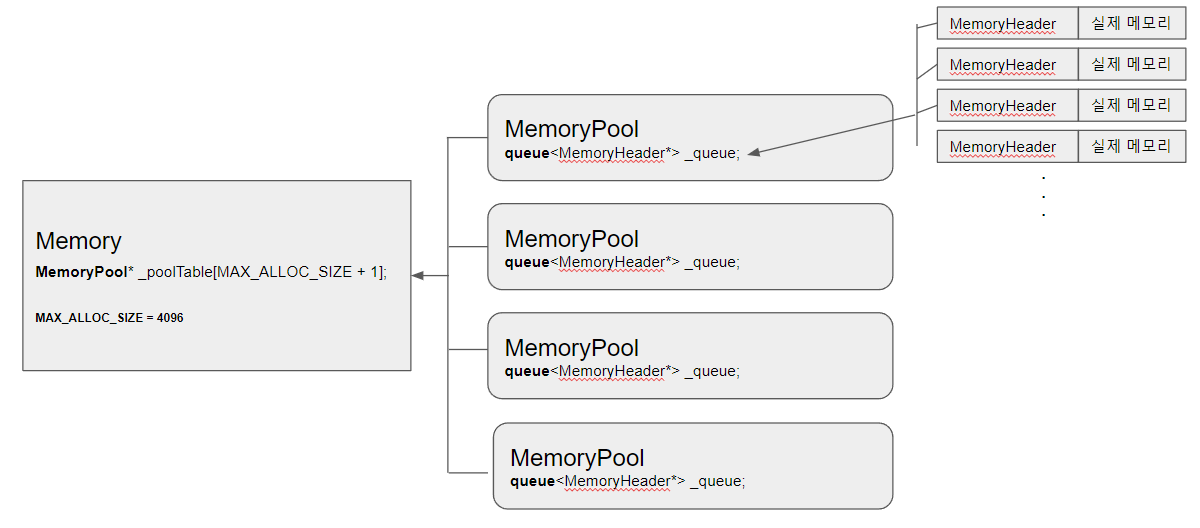
메모리 풀의 전체 구조는 아래와 같습니다
컨셉은 다양한 크기의 메모리를 메모리 풀화시켜서 사용 하는 방식입니다
주요 클래스는 다음과 같습니다
오른쪽 하단 부터 위쪽으로 화살표 방향대로 메모리를 생성하는 방향입니다
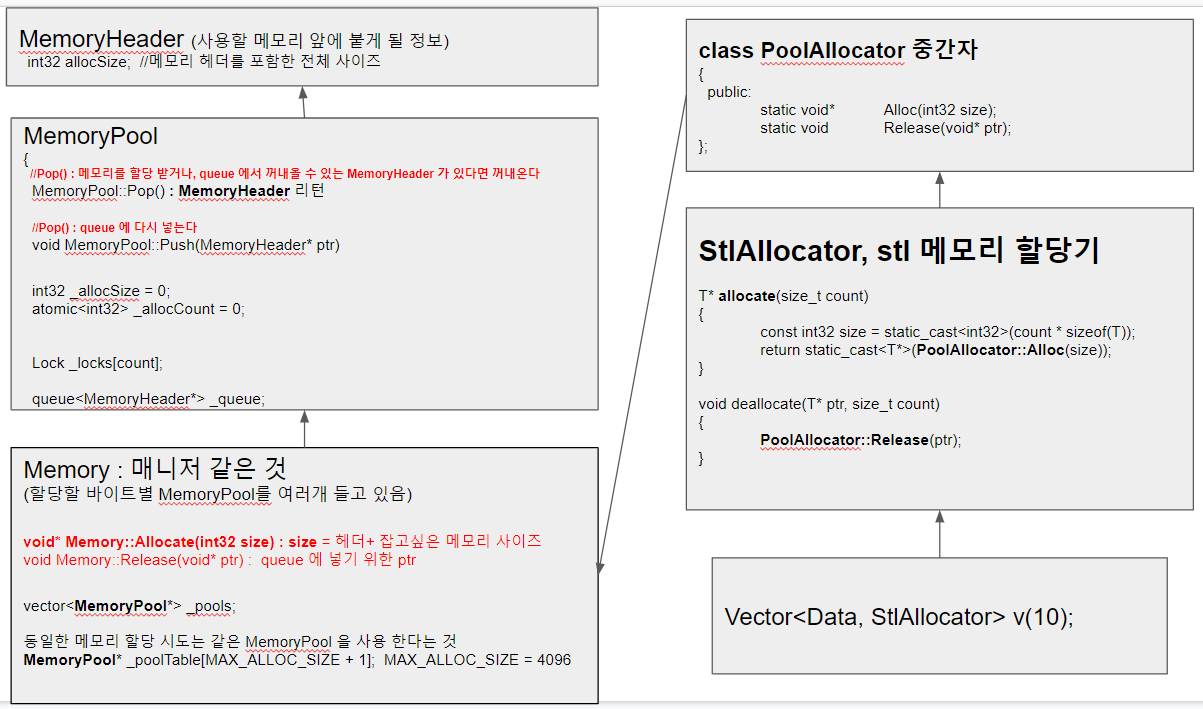
Thread-safe 한 형태
STL 에 사용할 Allocator
template<typename T>
class StlAllocator
{
public:
using value_type = T;
StlAllocator() { }
template<typename Other>
StlAllocator(const StlAllocator<Other>&) { }
T* allocate(size_t count)
{
const int32 size = static_cast<int32>(count * sizeof(T));
//return static_cast<T*>(xalloc__(size));
return static_cast<T*>(PoolAllocator::Alloc(size));
}
void deallocate(T* ptr, size_t count)
{
//xrelease__(ptr);
PoolAllocator::Release(ptr);
}
};
PoolAllocator : Memory 클래스를 경유하기 위한 중간 클래스
class PoolAllocator
{
public:
static void* Alloc(int32 size);
static void Release(void* ptr);
};
//어딘가에 있으면 됨
Memory* GMemory = nullptr;
void* PoolAllocator::Alloc(int32 size)
{
return GMemory->Allocate(size);
}
void PoolAllocator::Release(void* ptr)
{
GMemory->Release(ptr);
}
Memory : 메모리 풀 전체를 관장하는 메니저 유사한 것
메모리에는 메모리풀을 여러개 갖고 있다
//메모리에는 메모리풀을 여러개 갖고 있다
class Memory
{
enum
{
// ~1024까지 32단위, ~2048까지 128단위, ~4096까지 256단위
POOL_COUNT = (1024 / 32) + (1024 / 128) + (2048 / 256),
MAX_ALLOC_SIZE = 4096
};
public:
Memory();
~Memory();
void* Allocate(int32 size);
void Release(void* ptr);
private:
vector<MemoryPool*> _pools;
// 메모리 크기 <-> 메모리 풀
// O(1) 빠르게 찾기 위한 테이블
MemoryPool* _poolTable[MAX_ALLOC_SIZE + 1];
};
바이트가 적은 메모리를 보통 많이 사용하기 때문에 보다 적은 메모리를 사용 할경우에는
더 많이 사용 할 수 있도록 하고(queue개수 자체가 많아짐 queue.size() 를 말하는 것이 아님)
더 큰 공간을 사용할때는 개수 자체를 좀 줄이도록 하는데 큰 메모리를 pooling 할 일이 많진 않음으로 일반적으로
Memory::Memory()
{
int32 size = 0;
int32 tableIndex = 0;
for (size = 32; size <= 1024; size += 32)
{
MemoryPool* pool = new MemoryPool(size);
_pools.push_back(pool);
while (tableIndex <= size)
{
_poolTable[tableIndex] = pool;
tableIndex++;
}
}
for (; size <= 2048; size += 128)
{
MemoryPool* pool = new MemoryPool(size);
_pools.push_back(pool);
while (tableIndex <= size)
{
_poolTable[tableIndex] = pool;
tableIndex++;
}
}
for (; size <= 4096; size += 256)
{
MemoryPool* pool = new MemoryPool(size);
_pools.push_back(pool);
while (tableIndex <= size)
{
_poolTable[tableIndex] = pool;
tableIndex++;
}
}
}
Memory::~Memory()
{
for (MemoryPool* pool : _pools)
delete pool;
_pools.clear();
}
void* Memory::Allocate(int32 size)
{
MemoryHeader* header = nullptr;
const int32 allocSize = size + sizeof(MemoryHeader);
if (allocSize > MAX_ALLOC_SIZE)
{
// 메모리 풀링 최대 크기를 벗어나면 일반 할당
header = reinterpret_cast<MemoryHeader*>(::malloc(allocSize));
}
else
{
// 메모리 풀에서 꺼내온다
//Pop() : 메모리를 할당 받거나, queue 에서 꺼내올 수 있는 MemoryHeader 가 있다면 꺼내온다
header = _poolTable[allocSize]->Pop();
}
//= 할당할 메모리 가장 앞 부분을 MemoryHeader 영역으로 사용하고 그다음 MemoryHeader 이 사이즈 만큼 증가 시킨다음
//실제 vector 에서 사용할 메모리 번지를 void* 로 리턴 시킴
return MemoryHeader::AttachHeader(header, allocSize);
}
//해제 할때는 free 로 해제 하기 때문에 MemoryHeader가 시작되는 첫 주소를 역으로 받아와서 해제 하거나 다시 queue 에 넣는다
void Memory::Release(void* ptr)
{
MemoryHeader* header = MemoryHeader::DetachHeader(ptr);
const int32 allocSize = header->allocSize;
ASSERT_CRASH(allocSize > 0);
if (allocSize > MAX_ALLOC_SIZE)
{
// 메모리 풀링 최대 크기를 벗어나면 일반 해제
::free(header);
}
else
{
// 메모리 풀에 반납한다
_poolTable[allocSize]->Push(header);
}
}
MemoryPool : 실제 메모리 풀을 관리하는 클래스
class MemoryPool
{
public:
MemoryPool(int32 allocSize);
~MemoryPool();
void Push(MemoryHeader* ptr);
MemoryHeader* Pop();
private:
int32 _allocSize = 0;
atomic<int32> _allocCount = 0;
USE_LOCK;
queue<MemoryHeader*> _queue;
};
MemoryPool::MemoryPool(int32 allocSize) : _allocSize(allocSize)
{
}
MemoryPool::~MemoryPool()
{
while (_queue.empty() == false)
{
MemoryHeader* header = _queue.front();
_queue.pop();
::free(header);
}
}
void MemoryPool::Push(MemoryHeader* ptr)
{
WRITE_LOCK;
ptr->allocSize = 0;
// Pool에 메모리 반납
_queue.push(ptr);
_allocCount.fetch_sub(1);
}
MemoryHeader* MemoryPool::Pop()
{
MemoryHeader* header = nullptr;
{
WRITE_LOCK;
// Pool에 여분이 있는지?
if (_queue.empty() == false)
{
// 있으면 하나 꺼내온다
header = _queue.front();
_queue.pop();
}
}
// 없으면 새로 만들다
if (header == nullptr)
{
header = reinterpret_cast<MemoryHeader*>(::malloc(_allocSize));
}
else
{
ASSERT_CRASH(header->allocSize == 0);
}
_allocCount.fetch_add(1);
return header;
}
MemoryHeader : 사용할 메모리 앞에 붙는 헤더로 부가적인 정보를 붙일때 사용 할 수 있다
struct MemoryHeader
{
// [MemoryHeader][Data]
MemoryHeader(int32 size) : allocSize(size) { }
static void* AttachHeader(MemoryHeader* header, int32 size)
{
new(header)MemoryHeader(size); // placement new
return reinterpret_cast<void*>(++header);
}
static MemoryHeader* DetachHeader(void* ptr)
{
MemoryHeader* header = reinterpret_cast<MemoryHeader*>(ptr) - 1;
return header;
}
int32 allocSize;
// TODO : 필요한 추가 정보
};반응형